Centralized Management, Easy Control, Fast Response with i-frame
“Easy Administration” refers to a building block that represents centralized management, providing access and intervention to all components through the management panel of software platforms.
This concept enables processes to be managed in a streamlined, error-free and standardized manner.

The Difference Between Traditional Methods and i-frame
In traditional software systems, form, module, field, workflow and relationship definitions were usually done on separate screens, through complex menus and independent data models. This fragmented structure both wasted time and disrupted process integrity.
How i-frame Transforms This Process
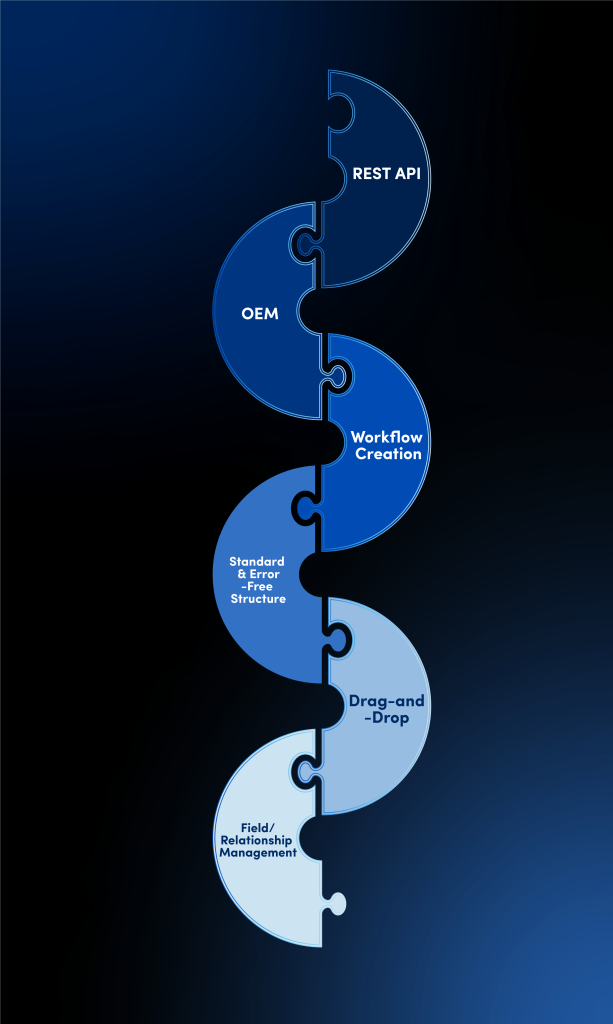
i-frame’s Easy Management module offers the ability to define and manage all the entities that form the backbone of a platform (module, form, field, process, relationship, list, filter, validation, notification, etc.) from a single point.
- All structures in a central panel: Module, field, relationship and process definitions are managed from a single screen.
- Drag-and-drop development: It crosses the boundaries of technical knowledge and enables business units to be productive.
- Standard and error-free structure: Minimizes repetitive work and enables the establishment of expandable systems without disrupting corporate memory.
- Dynamic updating and auditing: Fields, business rules and relationships can be edited instantly; all transactions are recorded.
- Secure content control with role-based management: Provides a sustainable management model with specific access and transaction permissions for each user.
Empowering businesses with flexible Easy Management solutions
Ease of Use and Integration Capability
| Feature | Traditional Methods | i-frame |
|---|---|---|
| Management Panel | Multiple menus and screens | Holistic access from a single screen |
| Module Definition | Done separately in layers with technical intervention | Drag-and-drop with visual interface and detailed configuration |
| Field/Relationship Management | May require code or database intervention | Field relations, data types, and bindings defined through interface |
| Workflow Creation | Requires external BPM engines or coding | Definition, triggers, and task setup with built-in process engine |
| Integration | Done at the database level | Quick connections via REST API and objects |
Key Features
Central Management Panel
One-stop access to all modules.
Object Association
Establishing relationships between fields and ensuring data integrity.
Effortless Module Construction
New module creation, content configuration, workflow definition.
Automation & Rules
Triggers, task schedules, email notifications.
List and Filter Management
View controls, dynamic queries.
Comprehensive Authorization
Role and user based access & transaction permissions.

Where is i-frame used?
- Corporate Internal Systems: All internal applications that manage form, approval and request workflows
- Government Applications: Centralized e-government solutions such as planning, application, tracking and document management
- OEM Product Infrastructures: Customizable product development for different brands thanks to low-code architecture
- Field and Industrial Solutions: Digitalization of IoT, production tracking, logistics, maintenance and quality processes
- Data Collection and Reporting Systems: Platforms that enable organizations to make decisions with data through dynamic dashboards and integrated reporting solutions

Who is using it?
- Developers: Can define complex structures without writing code.
- System Administrators: Can centrally oversee processes, areas and business rules.
- Business Units: Can update modules or define new content without the need for technical knowledge.
- Product Owners: Centrally analyze and update the live build of the product.

Advantages of Using i-frame
- Access all content from a single screen
- Centralized definition of modules, forms and processes
- Standardized information architecture
- Time savings in development and management
- Low error rate, high visibility
- Ease of use with no technical knowledge required
- Acceleration of information-based decision processes

